Precision Pediatric Caries Diagnostics: Saliva-Check Mutans versus Culture for High-Density Streptococcus mutans Detection
DISCOVERIES (ISSN 2359-7232), 2025, volume 13
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
FULL text (PDF)
CITATION: Gómez Rodríguez Z, Ramírez Thome SK, Díaz Castillejos R., García-Reyes ED, Martínez-Vargas A, Nájera-Segura NS, Jarquín González EE, Nivon-Torres GF, Acevedo Mascarua EA, Caballero-Sánchez H, Palacios Cruz RL, Solórzano-Mata CJ, Sosa-Velasco TA and Zárate-Ortiz C. Precision Pediatric Caries Diagnostics: Saliva-Check Mutans versus Culture for High-Density Streptococcus mutans Detection. Discoveries 2025, 13(4): e220; DOI: 10.15190/d.2025.19
Precision Pediatric Caries Diagnostics: Saliva-Check Mutans versus Culture for High-Density Streptococcus mutans Detection
Zeus Gómez Rodríguez1, Saira Karina Ramírez Thome1, Risk Díaz Castillejos1, Eunice Daysi García-Reyes1, Adrián Martínez-Vargas2, Nahui Samanta Nájera-Segura,3,2, Efrén Emmanuel Jarquín González4, Gilka Fernanda Nivon-Torres5,6, Enrique Alfonso Acevedo Mascarua1, Homero Caballero-Sánchez1, Roberta Lizette Palacios Cruz1, Carlos Josué Solórzano-Mata1,3, Taurino Amilcar Sosa-Velasco1, *, César Zárate-Ortiz1, *
- 1 Laboratorio de Bioquímica de Proteínas y Glicopatologías, Faculty of Dentistry, Universidad Autónoma "Benito Juárez" de Oaxaca, Oaxaca, Mexico
- 2 División de Estudios de Posgrado e Investigación, Tecnológico Nacional de México, Instituto Tecnológico del Valle de Etla, Abasolo S/N, Barrio del Agua Buena, Santiago Suchilquitongo, CP. 68030, Oaxaca, México
- 3 UNAM-UABJO Research Centre, Faculty of Medicine and Surgery, Universidad Autónoma Benito Juárez de Oaxaca (UABJO), Oaxaca 68120, Mexico
- 4 Dirección General de los Servicios de Salud de Oaxaca, Secretaria de Salud, Servicios de Salud de Oaxaca, Oaxaca, Mexico
- 5 Facultad de Ciencias Químicas, UABJO, 68120, Oaxaca, México, UABJO, Oaxaca 68120, Mexico
- 6 Facultad de Enfermería y Obstetricia Oaxaca (FAEO), UABJO, 68120, Oaxaca, México
* Corresponding authors: César Zárate-Ortiz, Laboratorio de Bioquímica de Proteínas y Glicopatologías, Faculty of Dentistry, Universidad Autónoma "Benito Juárez" de Oaxaca, Oaxaca, Mexico, Email: cesareoivo02@gmail.com and Taurino Amilcar Sosa-Velasco, Laboratorio de Bioquímica de Proteínas y Glicopatologías, Faculty of Dentistry, Universidad Autónoma "Benito Juárez" de Oaxaca, Oaxaca, Mexico, Email: asosa.faeo@uabjo.mx
Abstract
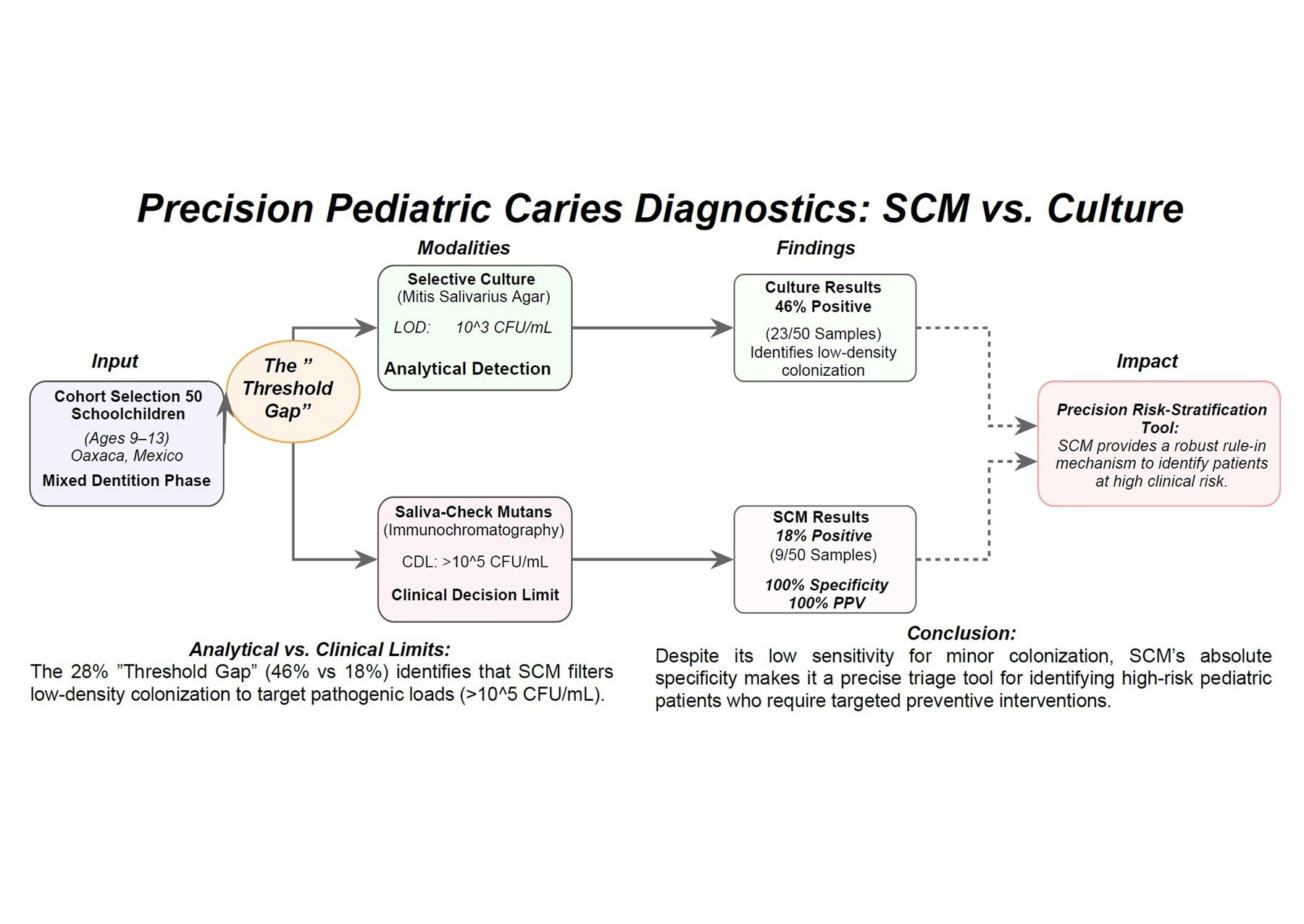
The paradigm of dental medicine is shifting from a reactive surgical model to precision pediatric caries diagnostics, emphasizing early detection of pathogenic oral microbiota. Rapid point-of-care assays capable of identifying high-density Streptococcus mutans are critical to enable targeted intervention. This pilot study evaluated the diagnostic validity of a high- threshold monoclonal antibody-based lateral flow assay (Saliva-Check Mutans, SCM) relative to selective culture for identifying clinically meaningful S. mutans loads in children. Stimulated saliva samples were collected from 50 schoolchildren aged 9-13 years in Oaxaca, Mexico. Samples were analyzed using SCM and selective culture on Mitis Salivarius Agar (MSA), with presumptive S. mutans colonies confirmed biochemically. Selective culture identified 46% of participants as positive, whereas SCM detected 18% as positive. Relative to culture, SCM demonstrated 39.1% sensitivity (95% CI: 21.5%–60.1%), 100% specificity (95% CI: 87.5%–100%), and 100% positive predictive value (95% CI: 66.4%–100%), with no false positives observed. The results highlight the assay’s rule-in capability for high-density pathogenic loads (>10^5 CFU/mL). The diagnostic discordance reflects divergent analytical thresholds, termed the “Threshold Gap”. While SCM exhibits limited sensitivity for low-level colonization, its absolute specificity supports its use as a precision high-threshold triage tool, identifying pediatric patients with clinically significant S. mutans burdens who may benefit from intensified preventive strategies. Integration with culture or molecular approaches can enhance risk stratification and precision dentistry workflows.